

To this end, we defined three key areas of interest in evaluating CBBCT. In the present study, our minimum acceptable benchmark in terms of radiation dose and lesion visualization is diagnostic mammography.
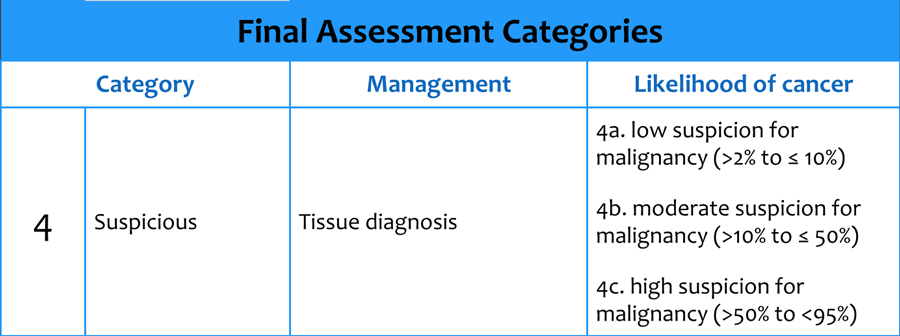
All lesions in this study were categorized under the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS ®) as category 4 or 5 lesions. This study represents a continuation of our earlier investigation, now turning our attention to the imaging of biopsy-proven pathology in mammographic lesions with high probability of malignancy by accepted mammographic and/or sonographical criteria. Our initial experiences with CBBCT have been previously reported. Cone-beam breast computed tomography (CBBCT) provides an additional imaging technique with a unique subset of advantages for diagnostic breast imaging. Technologies as varied as digital breast tomosynthesis and molecular breast imaging techniques such as positron emission mammography are presently under development, as are improvements in existing modalities such as ultrasound. In order to improve sensitivity and specificity of detecting and characterizing breast cancer, breast-specific imaging modalities are rapidly evolving. Although the mortality benefits of early cancer detection by screening mammography are indisputable, quantitative and qualitative limitations of mammographic technique, including the large size of lesions at initial detection and challenges of resolving subtle soft-tissue changes suggestive of cancer, are well documented in the literature. Early detection of breast cancer has been demonstrated to significantly decrease breast cancer mortality, even in women 40-49 years of age, despite the lower incidence of disease in younger cohorts. Owing to favorable radiation dose profile, excellent visualization of lesions, and qualitative benefits including improved patient comfort, excellent field-of-view, and more anatomical evaluation of lesion margins, CBBCT offers a promising modality for diagnostic evaluation of breast lesions.īreast cancer is most commonly diagnosed nonskin cancer in women and represents the second leading cause of cancer death in women of all ages and the leading cause of cancer mortality in women between 20 and 59 years of age. Our experience of side-by-side comparison of CBBCT and diagnostic mammography in BI-RADS ® 4 and 5 breast lesions demonstrated a high degree of correlation between the two modalities across a variety of lesion types. Patients reported greater comfort in CBBCT imaging relative to mammography. Characterization of high-risk lesions was excellent. Thirty-three of 34 mammographic lesions were scored as equally or better visualized in CBBCT relative to diagnostic mammography. 16.9 mGy (☖.9 SD) for diagnostic mammography in a total of 37 imaged breasts ( P<0.001). Results:ĬBBCT dose was similar to or less than diagnostic mammography, with a mean dose of 9.4 mGy (☓.1 SD) for CBBCT vs. Patients were administered a survey for qualitative evaluation of comfort between the two modalities. Mammograms and CBBCT images were compared side-by-side and lesion visibility/conspicuity was qualitatively scored. Administered radiation dose was calculated for each modality. Thirty-six consecutive patients (37 breasts) with abnormal mammographic and/or ultrasound categorized as BI-RADS ® 4 or 5 lesions were evaluated with CBBCT prior to biopsy. Usual screening follow-up is recommended.This pilot study was undertaken to compare radiation dose, relative visibility/conspicuity of biopsy-proven lesions, and relative patient comfort in diagnostic mammography and dedicated cone-beam breast computed tomography (CBBCT) in Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) ® 4 or 5 lesions. The radiologist should mention that it is a definite benign lesion. in neurofibromatosis type I (evidence of sarcomatous change is considered very low)Īlthough BI-RADS 1 and BI-RADS 2 both denote an essentially zero chance of malignancy, BI-RADS 1 is used in situations where the breast is completely unremarkable, and BI-RADS 2 is used when the radiologist wants to remark on a benign finding.Īny BI-RADS 2 breast finding is not expected to change over the follow-up interval. A finding placed in this category should have a 100% chance of being benign.Įxamples of such lesions or findings include:Ĭutaneous neurofibromas 3: e.g. BI-RADS 2 is a benign category in breast imaging reporting and data system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
